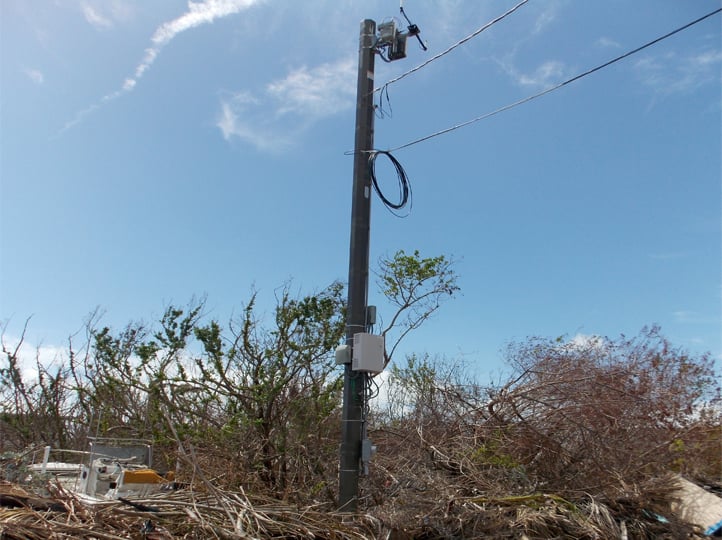
 Unscathed FRP utility pole after a hurricane
Unscathed FRP utility pole after a hurricane
Resiliency is one of the most used words these days. This is due to many reasons, including recognition that we need longer-lasting infrastructure and the extreme weather pushing infrastructure beyond the capacity of current materials and structures.
Common definitions of resiliency are:
- The capacity to recover quickly from difficulties; toughness
- The ability of something to return to its original size and shape after being deformed
There is a strong case for resilient infrastructure now. In the modern world that we live in, our infrastructure's resiliency is paramount for the safety and well-being of each citizen and the health of the economy. Our reliance on electricity and transportation systems to deliver electricity, goods and services has never been more apparent.
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) composites are well known for their lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistant attributes, but did you know they offer a high degree of resiliency or toughness?
FRP composites typically exhibit high strength in bending with a moderate modulus of elasticity. Some engineers view the lower stiffness as a structural liability, even though they should not. Strength and deflection are always part of a structural design requirement. Regardless of the material of construction, these critical design elements must be met. Composites are designed to satisfy code requirements while providing a tremendous amount of resiliency to the structure.

Applications that are affected by impact can greatly benefit from composite materials. The combination of high strength and moderate stiffness means that the strain energy of the material absorbs impact energy. A few applications in which engineers and owners are taking advantage of the energy absorption capacity of composites include bridges, docks, ferry terminal fendering systems, and electrical distribution and transmission poles.
FRP utility poles are ideal for grid reliability enhancement. They are resilient in terms of taking a significant load during a major event and returning to their normal state. In addition, FRP poles can absorb about 10x the energy of a steel pole with similar geometries.
The area under the load-deflection curve is the 'indicative resiliency' or toughness of a material. For example, the graph below depicts typical load-displacement curve areas or energy absorption capacities of steel and wood poles.
The definition of resiliency aptly describes one of the benefits of FRP composites. Utility poles are just one example where this material contributes to improving the resiliency of our infrastructure.
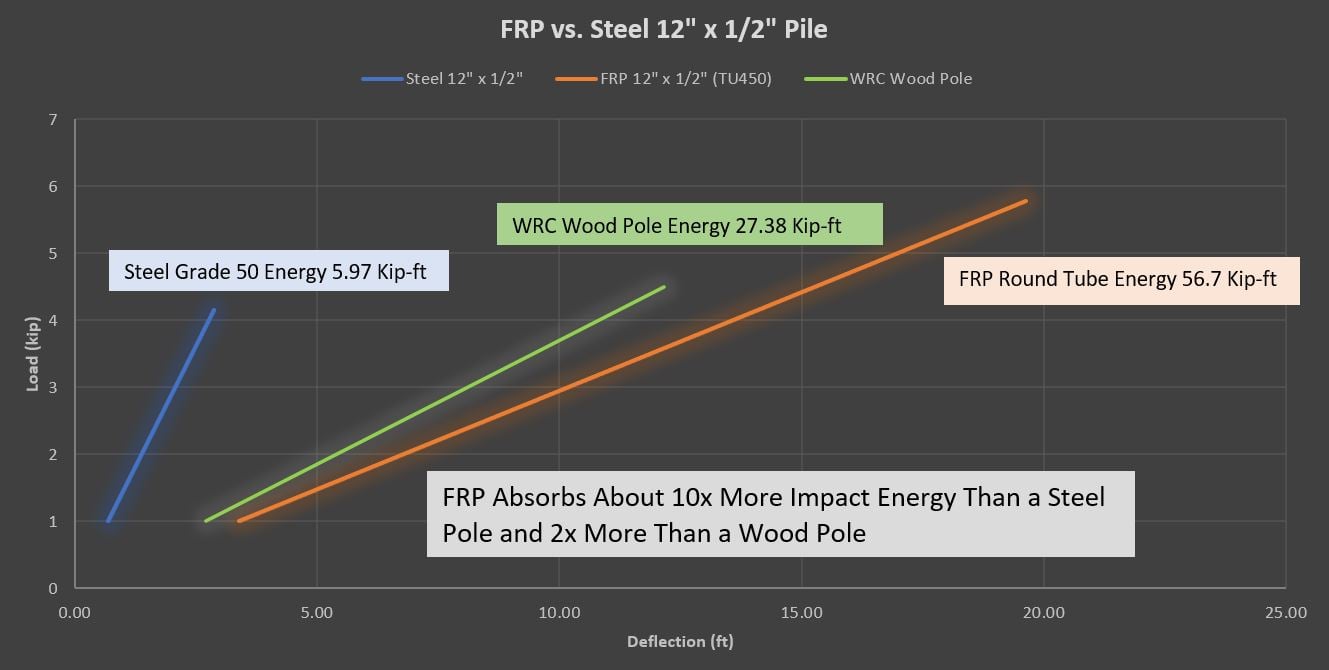
In this example, the poles are assumed to be 60’ in length and buried approximately ten feet into the ground as a cantilever structure. The poles were loaded to ANSI Class 1 load requirements. After calculating the area under the curve, the FRP pole exhibited about 10x the energy capacity of a steel pole and about 2x the energy capacity of a wood pole while satisfying the industry deflection requirements.
If you have a project that would greatly benefit from FRP composite's resiliency, please get in touch! We'd love to hear about it.
